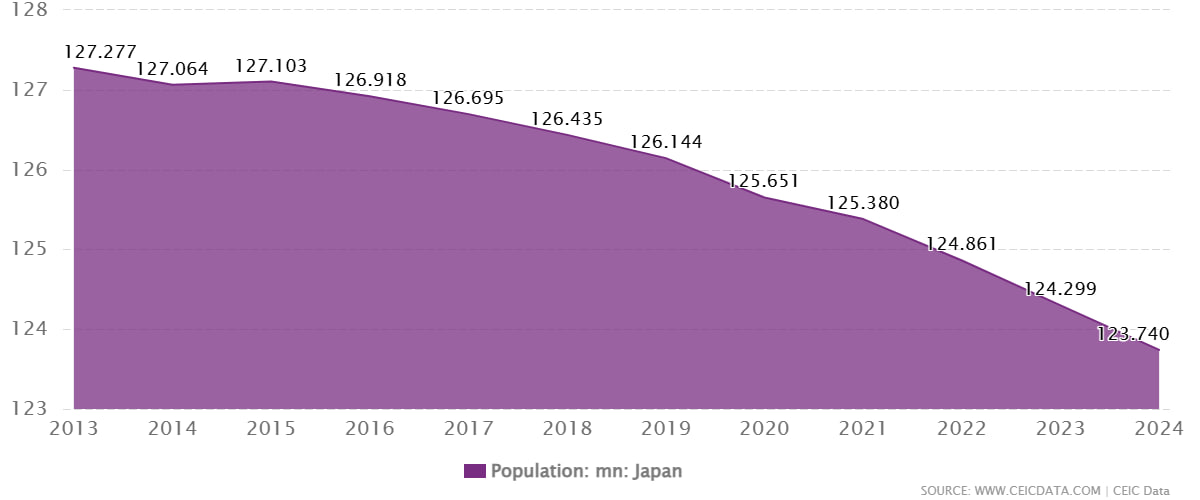
Japan is facing a significant demographic crisis as its population continues to decline at an unprecedented rate. This ongoing trend poses serious challenges for the country’s economy, workforce, and social systems. In this article, we will explore the causes, effects, and potential solutions related to Japan’s population drop.
Causes of Japan’s Population Decline
Several factors contribute to Japan’s shrinking population. One of the main reasons is the country’s low birth rate. Many young couples in Japan are delaying marriage and childbearing due to economic pressures, career priorities, and changing social norms. Additionally, Japan has one of the highest life expectancies in the world, leading to an aging population where the number of elderly far exceeds that of newborns.
Another factor is limited immigration. Japan traditionally maintains strict immigration policies, resulting in fewer young workers entering the country to offset the declining native population.
Economic Impact of Population Decline
The falling population has deep repercussions for Japan’s economy. With fewer working-age individuals, companies face labor shortages that hinder productivity and growth. Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and technology are particularly affected.
Moreover, the shrinking consumer base reduces domestic demand for goods and services, impacting businesses and overall economic vitality. The government also faces increasing pressure to fund pensions and healthcare for the growing elderly demographic.
Social Challenges and Infrastructure
A declining and aging population places stress on Japan’s social services and infrastructure. Rural areas are particularly hard hit as young people migrate to urban centers, leaving behind communities with dwindling populations. This trend threatens the sustainability of schools, hospitals, and transportation systems in less populated regions.
The government must find ways to maintain social cohesion and support systems while adapting to these demographic shifts.
Possible Solutions and Future Outlook
Japan is exploring multiple strategies to mitigate the effects of its population decline. These include policies to encourage higher birth rates, such as improved childcare support, parental leave, and financial incentives for families.
Additionally, there have been gradual relaxations in immigration rules to attract foreign workers, especially in sectors facing acute labor shortages.
Technological innovations like robotics and artificial intelligence are also being leveraged to supplement the workforce and care for the elderly.
Despite these efforts, reversing the population decline remains a formidable challenge, requiring long-term commitment and multifaceted approaches.
Conclusion
Japan’s population continues to plummet due to a combination of low birth rates, an aging society, and limited immigration. This demographic trend impacts the economy, social infrastructure, and national sustainability. Addressing this issue demands comprehensive policies that support families, open avenues for immigration, and harness technology to build a resilient future.